Here’s a new OB page.
Have been expanding, updating, and rearranging it. But there’s always more to do.
Here’s a new OB page.
Have been expanding, updating, and rearranging it. But there’s always more to do.
Posted in Order-of-Battle
Sergey Shoygu had news on the Russian Airborne Troops at yesterday’s collegium.
The Defense Minister claimed the Pskov-based 76th DShD will get its third air-assault regiment this year.
The Kamyshin-based 56th Air-Assault Brigade will consolidate to a regiment by the end of 2021 and redeploy to Feodosia.
There (presumably) it’ll join up with the battalion based there to become the third regiment of Novorossiysk’s 7th DShD.

The 56th was a Ground Troops formation before its handover to the VDV in 2013.
The MOD and VDV have long talked of returning to the traditional three maneuver regiment structure in airborne (air assault) divisions. It’s taken quite a while.
In Pskov, finding manpower, equipment, and housing won’t be easy. In the south, fleshing out the 7th DShD costs a brigade but makes sense. Still its redeployment won’t be trivial.
What else from Shoygu?
Besides raising their “combat potential,” the VDV are also upgrading their C2 system and infrastructure in Crimea, Pskov, and Omsk (242nd Training Center), Shoygu said.
The last OOB spreadsheet didn’t have much on the Eastern MD’s air forces (i.e. the 11th AVVSiPVO).
The 303rd Composite Aviation Division’s subordinate regiments are now included.
One is the 18th Guards Assault Aviation Red Banner Regiment based at Chernigovka.
Chernigovka last October
Some number (probably not two complete squadrons) of Su-25SM ground attack aircraft are parked along the flight line and on hardstands.
In 2015, Bmpd reposted an item from Alexeyvvo indicating this regiment was second (after Budennovsk — Southern MD) to receive the modernized Su-25SM.
Mil.ru confirmed the presence of an assault aviation regiment at Chernigovka in late 2019.
The helicopters on hardstands belong (ostensibly at least) to the 319th Independent Helicopter Regiment. Russian sources say the regiment has roughly 20 Ka-52 and 20 Mi-8AMTSh — either two large squadrons or maybe four smaller squadrons — two of each type (??).
The regiment has the same v/ch as the old 575th Aviation Base which can be considered replaced. The aviation bases were an innovation from Anatoliy Serdyukov’s tenure intended to save money by operating several aircraft types from the same airfield. It wasn’t popular with the aviators.
But a legacy from this is two different aviation units sharing the base at Chernigovka.
Muddying the waters is Mil.ru from early 2019 indicating there’s an army aviation formation [soyedineniye] at Chernigovka. Or a resurrected (and as yet unidentified) army aviation brigade.
For now let’s call it the 319th Regiment though now it’s probably a u/i brigade. Four smaller helo squadrons would make more sense as a brigade than a regiment.
Supporting the notion that the old 575th has reverted to an army aviation brigade, the old 573rd Aviation Base at Khabarovsk-Tsentralnyy airport is now the 18th Army Aviation Brigade with Ka-52, Mi-8AMTSh, and Mi-26 helos.
Similarly, in 2018, the VKS transformed the Central MD’s aviation bases into an army aviation brigade and an independent helo regiment.
These are largely organizational changes; the equipment has remained pretty much the same. But that’s some of the process of following the OOB. And here is the latest OOB, never finished, always a work in progress.

ROC priest blesses BMD-4M delivered in January
Russia’s VDV got its ninth battalion set of new BMD-4M and BTR-MDM armored vehicles on June 19, according to media in Pskov — home of the 76th Air-Assault Division’s 234th Air-Assault Regiment. The tenth battalion set will reach troops in Stavropol before the end of 2020, according to the Russian Defense Ministry.
Here’s some info on when and where these new airborne infantry fighting vehicles and personnel carriers were delivered.
Click on the image for a larger table where you can click the links therein.
Posted in Defense Industry, Force Modernization, Order-of-Battle, VDV
Tagged Airborne Troops, BMD-4M, BTR-MDM

At the MOD Collegium on March 20, Russian Minister of Defense Sergey Shoygu pretty much acted like there’s not reason for concern.
With pandemic set to sweep across Russia (everywhere else too), Mr. Shoygu outlined the MOD plan to manage coronavirus. Most of his publicized remarks still focused on the country’s military security and the “increased presence” of U.S. forces, ships, and planes on Russia’s borders.
Shoygu claimed no COVID-19 cases in the Russian Army. The MOD has stopped sending “military delegations” abroad and it won’t host foreign officers. He mentioned vague plans to keep Russian troops close to their garrisons.
Russia’s spring draft won’t be postponed. It will begin as normal on April 1 and end July 15. Conscripts will be tested for coronavirus before they go to their units, and “isolated” during their first two weeks there.
How about testing young men before they answer the summons at the military commissariat? The draft is good news for men being demobbed. Not so good for their replacements.
Recall the Russian Army is a place where barracks and units have been decimated by illness in the recent past. Sixty percent of disease there is respiratory (as is COVID-19). The MOD’s medical establishment is often corrupt and probably just average on its best day.
So much for health security . . . . The Collegium turned to the 2020 plan of activity for the Southern and Eastern Military Districts. After describing U.S. efforts to dominate Russia’s “south-west strategic direction” and the Black Sea, Shoygu said the Southern MD got 1,200 new and modernized weapons and equipment in 2019, and will get nearly three times that many in 2020.
The Defense Minister said the Southern MD will stand up a motorized rifle division and two “missile troops and artillery” brigades. Perhaps the Russians will upgrade one of the Stavropol-based 49th CAA brigades to division status.
“Missile troops and artillery” is the formal name for the artillery branch of the Ground Troops. It seems likely one artillery brigade will be established at the district level and another for the 8th CAA.
After detailing U.S. striving to control the Asia-Pacific region as well as Russia’s Sakhalin and Primorye “operational directions,” Shoygu indicated the Eastern MD got 1,300 major items of equipment in 2019, and will get 1,350 including 502 new ones (so 848 modernized) this year.
He said the Eastern MD will get motorized rifle and tank regiments (probably just one of each) in Primorye. They will likely round out the 5th CAA’s 127th MRD, created recently out of the 59th MRB.

127th MRD at Sergeyevka
Shoygu also said the Eastern MD will participate in nine international training events in 2020. The MOD also remains adamant that the 75th Victory Day celebration will go on no matter what. Not sure how that squares with health security. Sounds like mixed messaging by the MOD.
Posted in Conscription, Force Modernization, Ground Troops, Military Medicine, Order-of-Battle
Tagged Collegium, Coronavirus, COVID-19, Eastern MD, Sergey Shoygu, Southern MD
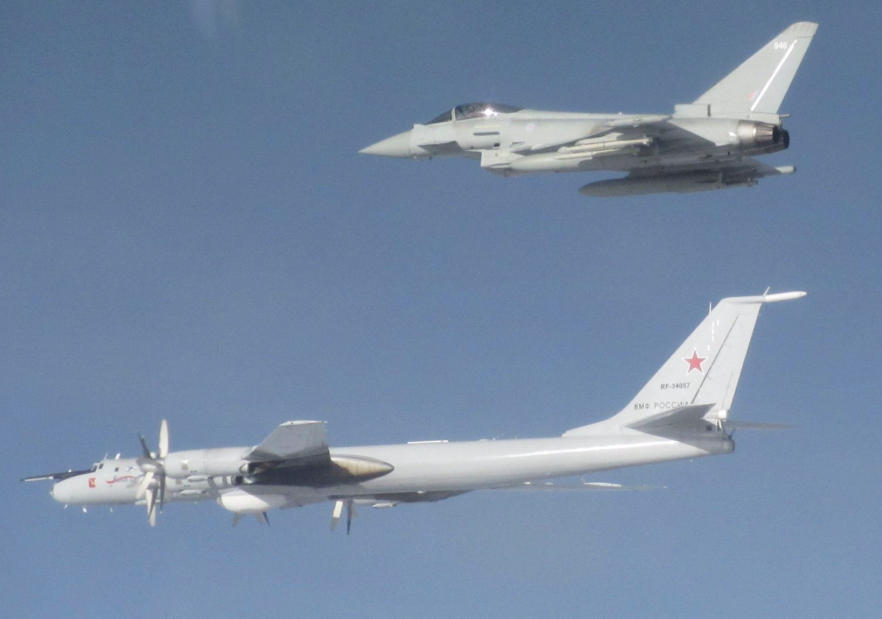

RAF Typhoon intercepts Bear F
Russia’s Tu-142 / Bear F ASW aircraft are waking up at the end of the winter training period. The Russian media highlighted four evolutions recently.
We probably haven’t seen a surge in long-range naval surveillance flights like this in some time. Possibly not since Soviet times.
On March 7, two Bear F flew a patrol into the Atlantic. A Russian Northern Fleet spokesman said the aircraft were refueled over the southern Norwegian Sea during the 15-hour flight. The aircraft trained over waters near Spain and Portugal before returning home.
On March 6, three Pacific Fleet Bear F over the Sea of Japan practiced locating, tracking, and attacking a notional enemy submarine.
On March 4, at least one (probably more) Bear F aircraft was refueled over the Black Sea. TVZvezda provided this video. Northern Fleet air crews trained at the Russian Navy’s Combat Training and Combat Employment Center in Yeysk during the week.
On 26-27 February, two Bear F flew a mission south of the Faeroes and Iceland, possibly to gain contact on U.S. or British subs enroute to ICEX 2020.
At present, there are likely about 24 Tu-142 aircraft in the Russian Naval Aviation inventory. One air group or squadron of 12 each (possibly as many as 15) in the Northern and Pacific Fleets. The former at Kipelovo-Fedotovo and the latter at Mongokhto.

In the late 1960s, the Tupolev design bureau developed the Tu-142 on the blueprint of the Tu-95 / Bear bomber with a range of roughly 10,000 km.
The Bear F has carried various ASW systems including surface search radars, airborne acoustic detectors, Korshun search-targeting system, magnetic anomaly detectors, IR direction finders, gas analyzers, and Korshun-K. The Korshun-K system is found on the Tu-142MK. The Tu-142MZ is distinguished by its newer NK-12MP engines.
The Bear F, while aged in most cases, has been a reliable aircraft. It’s suffered three known crashes, the last in 2009 occurred in the Strait of Tatary.
The current fleet was produced mainly in the late 1970s and 1980s. A number, perhaps most, of them received capital repairs in the late 2000s and 2010s.
The oldest Russian Bear F are likely 40-45 years old. The youngest perhaps 30. But relatively restricted flying hours have helped keep them in the air. Flying them hard, however, would stress the limits of the force.
The Russian Navy is reportedly thinking about acquiring civilian Tu-204 or Tu-214 airliners for conversion into new ASW aircraft but this would be expensive and hasn’t advanced beyond the requirements stage yet.
Posted in Navy, Order-of-Battle, Training and Exercises
Tagged Anti-Submarine Warfare, ASW, Bear F, Il-78, Naval Aviation, Tankers, Tu-142, Tu-142MK, Tu-142MZ
St. Petersburg is probably now Russia’s second best protected city in terms of air defense (as common sense would dictate).
Interfaks-AVN reported today that another regiment of the Western MD’s 2nd Air Defense Division in Leningrad oblast has completed training with the S-400 to include combat firings against Favorit targets (the 5V55 missile from the S-300P system).
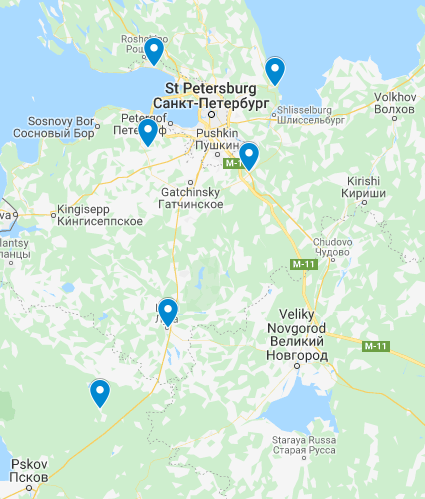
S-400 deployments in the 2nd ADD
The regiment, likely the 1489th SAM Regiment, has returned to its home base of Vaganovo ENE of StP. It’s supposed to begin combat duty in February 2020, according to Interfaks-AVN.
The 500th SAM Regiment at Gostilitsy WSW of StP got its S-400s in 2015. The 1488th at Zelenogorsk NW of StP in 2016, the 1490th at Ulyanovka SE of StP probably in 2017, and the 1544th at Vladimirskiy Lager (but launch battalions split between Luga and Strugi Krasnyye) S of StP in 2018.
So not only is the 2nd ADD now all S-400, it’s also a five-regiment SAM division.
Here’s a handy reference to S-400 deployments (which have been difficult to keep up on). No wonder Mr. Putin wants to unplug the Internet and get rid of ru.wikipedia.org.
Posted in Aerospace Forces, Force Modernization, Order-of-Battle
Tagged 2nd Air Defense Division, S-400
Here’s a look at one Russian motorized rifle brigade, created for another purpose, but perhaps worth sharing. The Kamenka brigade’s appeared on these pages before but mainly because of its order and discipline problems.
The 138th Independent Motorized Rifle Brigade (v/ch 02511) is based in Kamenka village, Vyborg rayon of Leningrad oblast. Its full honorific name is the 138th Independent Guards Motorized Rifle Krasnoselskaya Order of Lenin Red Banner Brigade. 138th IMRB for short.

The brigade’s lineage goes to the 45th Guards Rifle Division. That formation participated in the liberation of German-occupied Krasnoye Selo in January 1944.
The division’s regiments (now battalions) received the Leningrad honorific for fighting to lift the German blockade of the city.
The 138th IMRB is part of the 6th Combined Arms Army and the Western Military District.
The following units are subordinate to the 138th IMRB:

Construction of new facilities at Kamenka in 2016
Today’s IMRB should have nearly 4,000 personnel compared to a nominal 2,500-man motorized rifle regiment (MRR). While the maneuver battalions are similar, the IMRB is heavier in fire support, combat support, and service sub-units [подразделения – battalion or lower]. It has two self-propelled howitzer battalions and an MLRS battalion against the single battalion of towed 122-mm D-30 howitzers in Soviet regiments.
The IMRB’s anti-aircraft and anti-tank capabilities are organized in battalions. They used to be single batteries in old MRRs. Most of today’s combat support and service is provided by battalions compared with companies in Soviet times. The old MRR relied more on support and service from the division level.
The 138th IMRB’s motorized rifle battalions have about 500 personnel with about 100 men in each of three companies operating ten MT-LB light armored vehicles. A battalion probably has 31 MT-LBs. The MT-LB is also the prime mover for other sub-units, so the brigade has a significantly larger total inventory, often put at 159 in all. For example, artillery battalions have eight each and anti-tank gun batteries have six.
The 138th is one of several MR brigades primarily using venerable MT-LBs rather than more modern BTRs or BMPs. The 25th near Pskov is another. Others are in mountainous areas of the North Caucasus or in the Eastern MD. The Russian Army may like the MT-LB’s performance in the marshy terrain of Leningrad oblast. At any rate, it’s a simple, reliable armored vehicle that the MOD still has in large numbers.
For integral fire support, each motorized rifle battalion has a battery of six towed 120-mm 2B16 Nona-K gun-mortars in two firing platoons of three weapons. The battalion has a man-portable 9K115 Metis ATGM battery of three platoons of three launchers. The battalion has an air defense battery organized similarly with three platoons of three hand-held 9K38 Igla SAMs.
The 138th IMRB’s tank battalion is outfitted with 41 T-72B3 tanks, ten tanks in each of four tank companies.
The brigade’s two SP howitzer battalions are organized in traditional fashion – 18 152-mm 2S3 Akatsiya systems in three batteries of two platoons with three guns each. The MLRS battalion with 18 122-mm BM-21 Grad systems is similar with three batteries, two platoons of three vehicles.
The brigade’s anti-tank battalion has two batteries of six towed 100-mm MT-12 Rapira guns and six 9P149 Shturm-S ATGMs. The batteries have two firing platoons with three weapons. The anti-tank guns are towed by MT-LBs, and the ATGMs are mounted on MT-LBs.
The brigade SAM battalion has three launch batteries of four 9K332M Tor-M2 SAMs. It has a battery with two launch platoons of three 9A34 Strela-10 SAMs, and probably a battery (two three-vehicle platoons) of older remaining 2S6 (9K22) Tunguska gun-missile systems.
Overall, the 138th IMRB is a pretty average formation that hasn’t been particularly favored with equipment upgrades or modernization.
Posted in Cheap Posts, Ground Troops, Order-of-Battle
Tagged 138th MRB, Kamenka, Krasnoselskaya, MT-LB
RG gave us the scantest info. The Russian Army is upgrading an independent tank battalion to a regiment in Smolensk oblast, in the Western MD. The new regiment will belong to one of the 20th CAA’s motorized rifle divisions.
It reportedly will be outfitted with T-72BA tanks, BMP-2 AIFVs, engineer and repair-recovery vehicles, air defense, and recce.
According to RG, the 20th CAA is the largest “large formation” [объединение — anything above a division] in Russia’s armed forces. It is deployed along Russia’s western border in Belgorod, Bryansk, Voronezh, Kursk, and Smolensk oblasts.
Then one has to scrounge. There’s info of varying quality and completeness available. Sometimes you find something like this or this.
The new tank regiment will be part of the 144th Motorized Rifle Division, based in Smolensk and Bryansk oblasts. The 144th at present may look like this:
In the first link above, Yuriy Barash, a Ukrainian observer, maintains in 2017 the 144th began forming up its 182nd MRR, 228th TR, and 1259th SAM Regiment as well as anti-tank, material support, and medical battalions. It had not started forming up the 254th MRR or the specialist companies, according to him.

So does the 228th Tank Regiment already exist? No and yes.
If Barash’s TO&E for the 144th isn’t wrong (but it could be), the 448th MRR and 856th SP Artillery Regiment appear to be its only fleshed out and combat-capable units. In 2017, he held only 40 T-72s in the division (the tank battalion of the 448th).
CAST, however, suggested that the 144th has an independent tank battalion that will be upgraded to a regiment, to become the 228th TR.
There are also discrepancies regarding the locations of different units.
Welcome to following Russia’s OOB.
Here’s the moral. Saying you have a division on your western border is one thing; actually having one is something else.
Posted in Ground Troops, Order-of-Battle
Tagged 144th MRD, 20th CAA, 228th Tank Regiment, Klintsy, Smolensk, Yelnya
Here’s a link to a new version of the OOB notes. It has several pages of new info and other changes and corrections. It’s a short version of a longer spreadsheet you can view here.
The longer file has formation honorifics, military unit (в/ч) numbers, four levels of subordination, some info on weapons and equipment holdings, and bitlinks to good sources.
Posted in Order-of-Battle